A continual learning survey: Defying forgetting in classification tasks
2021 TPAMI 올라온 survey.
Journal들은 조금 outdated 되었지만, archivable 한 자료들이라 원리적인 내용이 풍부하다는 교수님 말씀.
TLDR
아는 친구들 몇 개와 수 많은 모르는 친구들
Quick Look
- Authors & Affiliation: Matthias De Lange
- Link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.08383.pdf
- Comments: TPAMI
- Relevance: 3
Research Topic
- Category (General): Continual Learning
- Category (Specific): Continual Learning, Survey
Paper Summary (What)
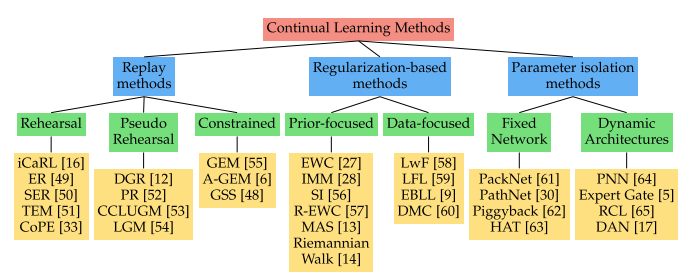
- Replay methods
This line of work stores samples in raw format or generates pseudo-samples with a generative model.
These previous task samples are replayed while learning a new task to alleviate forgetting.- Rehearsal methods explicitly retrain on a limited subset of stored samples while training on new tasks. (icarl)
- constrained optimization : constrain new task updates to not interfere with previous tasks.
This is achieved through projecting the estimated gradient direction on the feasible region
outlined by previous task gradients through first order Taylor series approximation. - pseudo rehearsal is an alternative strategy used in early works with shallow neural networks.
The output of previous model(s) given random inputs are used to approximate previous task samples
- Regularization-based methods
This line of works avoids storing raw inputs,
extra regularization term is introduced in the loss function,
consolidating previous knowledge when learning on new data.- Data-focused methods : knowledge distillation,
vulnerable to domain shift between tasks - Prior-focused methods :
prior-focused methods estimate a distribution over the model parameters,
used as prior when learning from new data. - Prior-focused methods typically,
importance of all neural network parameters is estimated,
with parameters assumed independent to ensure feasibility.
During training of later tasks, changes to important parameters are penalized.
- Data-focused methods : knowledge distillation,
- Parameter isolation methods
Different model parameters to each task, to prevent any possible forgetting.
One can grow new branches for new tasks, while freezing previous task parameters
or dedicate a model copy to each task
Alternatively, the architecture remains static, with fixed parts allocated to each task. - 앞으로도 숙제가 이만큼!

나 졸업하기 전에 해결되면 좆되는 목록 - 다른 분야와의 비교
Notable References
Thoughts
Continual Learning with Filter Atom Swapping 같은 memory-based methods는 소개 없음!
저널을 쓰기 시작했을 당시에만 해도 최신 이었는데 벌써 outdated, 발전 속도가 너무 빠르다
Footnote
아래와 같은 양식을 활용한다.
#
## Quick Look
- **Authors & Affiliation**: [Authors][Affiliations]
- **Link**: [Paper link]
- **Comments**: [e.g. Published at X / arXiv paper / in review.]
- **TLDR**: [One or at most two line summary]
- **Relevance**: [Score between 1 and 5, stating how relevant this paper is to your work. Usually filled in at the end.]
# Research Topic
- **Category** (General):
- **Category** (Specific):
# Paper Summary (What)
[Summary of the paper - a few sentences with bullet points. What did they do?]